Carbohydrates are organic compounds composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. They are one of the three main macronutrients essential for the human diet, alongside proteins and fats. Carbohydrates play a crucial role in providing energy for various biological processes and are a primary source of fuel for the body.
Carbohydrates can be classified into three main types:
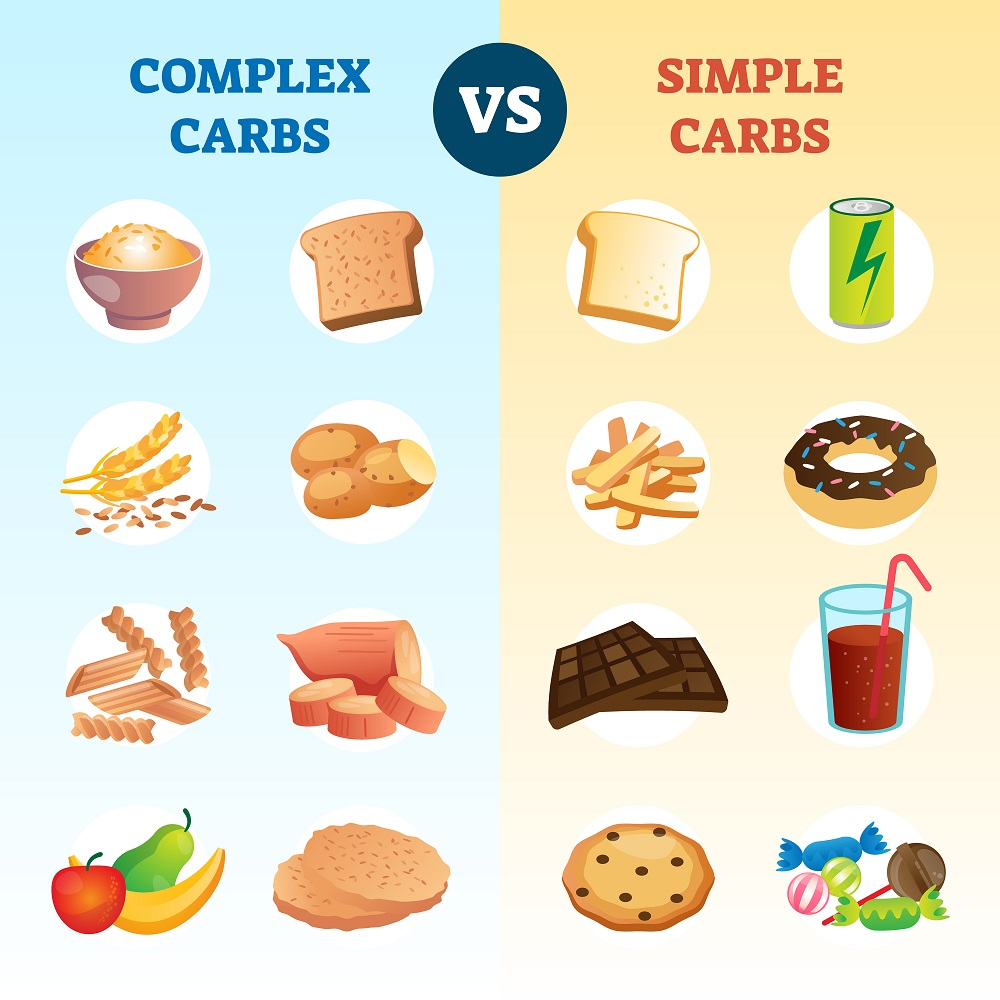
- Simple Carbohydrates (Sugars): These are composed of one or two sugar units. Examples include glucose, fructose, and sucrose. Simple carbohydrates are found in foods like fruits, honey, and table sugar.
- Complex Carbohydrates (Starches and Fiber): These are made up of multiple sugar units and can be further divided into starches and fibers.
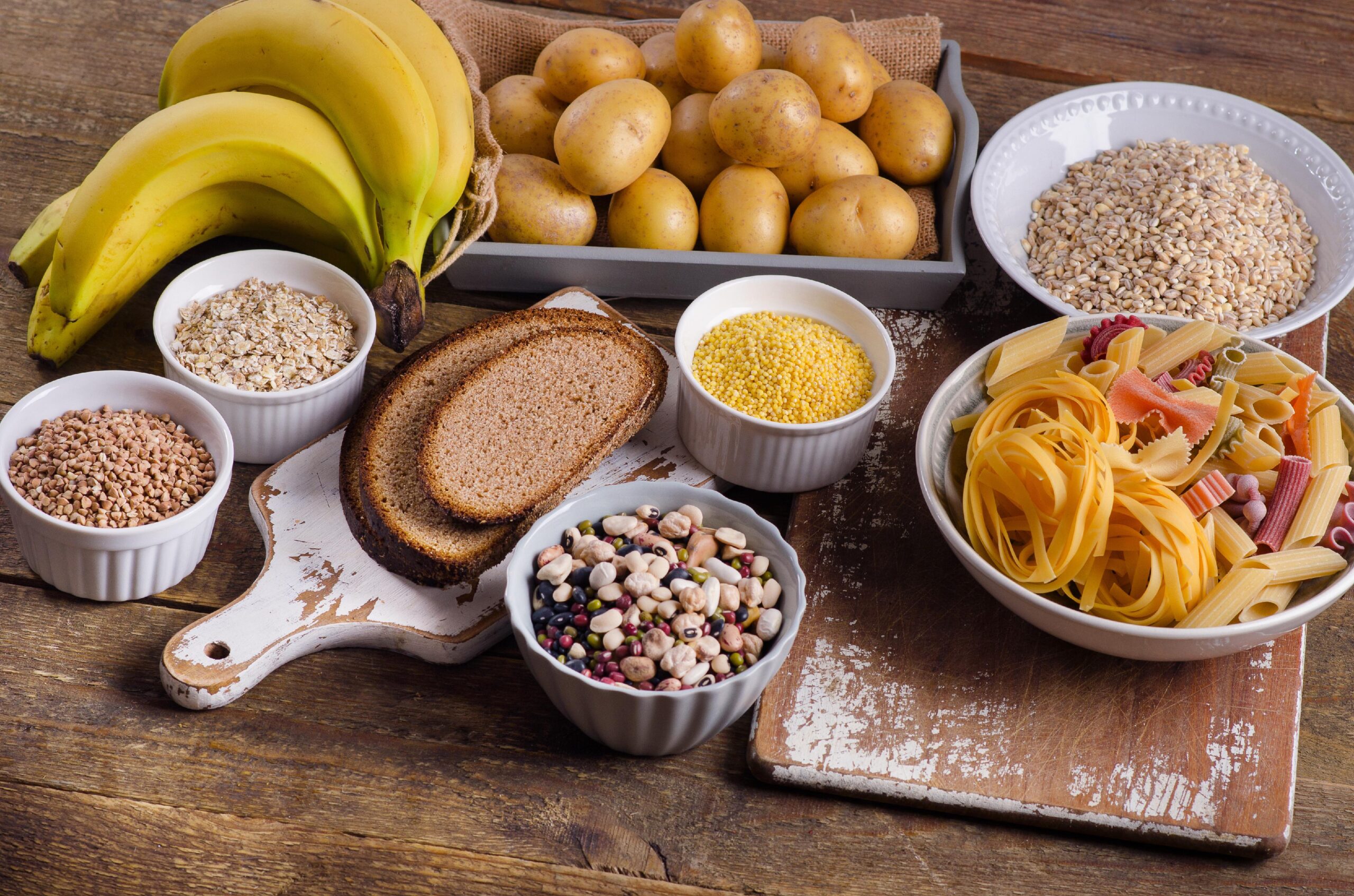
- Starches: Complex carbohydrates found in foods like grains, legumes, and tubers. They are broken down into simpler sugars during digestion.
- Fiber: This includes both soluble and insoluble fiber, which are not fully digested by the body. Sources of fiber include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes.
Carbohydrates are a primary source of energy for the body. When consumed, they are broken down into glucose (or other simple sugars) through digestion. Glucose is then utilized by cells for energy production. It’s worth noting that not all carbohydrates are created equal, and the quality of carbohydrates in a diet can impact health. Choosing complex carbohydrates with high fiber content is generally considered healthier than consuming excessive amounts of simple sugars.
Common foods with carbohydrates include:
- Grains, such as bread, noodles, pasta, crackers, cereals, and rice
- Fruits, such as apples, bananas, berries, mangoes, melons, and oranges
- Dairy products, such as milk and yogurt
- Legumes, including dried beans, lentils, and peas
- Snack foods and sweets, such as cakes, cookies, candy, and other desserts
- Juices, regular sodas, fruit drinks, sports drinks, and energy drinks that contain sugar
- Starchy vegetables, such as potatoes, corn, and peas